Prediction of Cerebral Aneurysm Rupture using a Point Cloud Neural Network
Xiaoyuan Luo*, Jienan Wang*, Xinmei Liang, Lei Yan, Xinhua Chen, Jian He, Jing Luo, Bing Zhao, Guangchen He; Manning Wang†, Yueqi Zhu†
Journal of NeuroInterventional Surgery (2022, IF=5.836)
Abstract
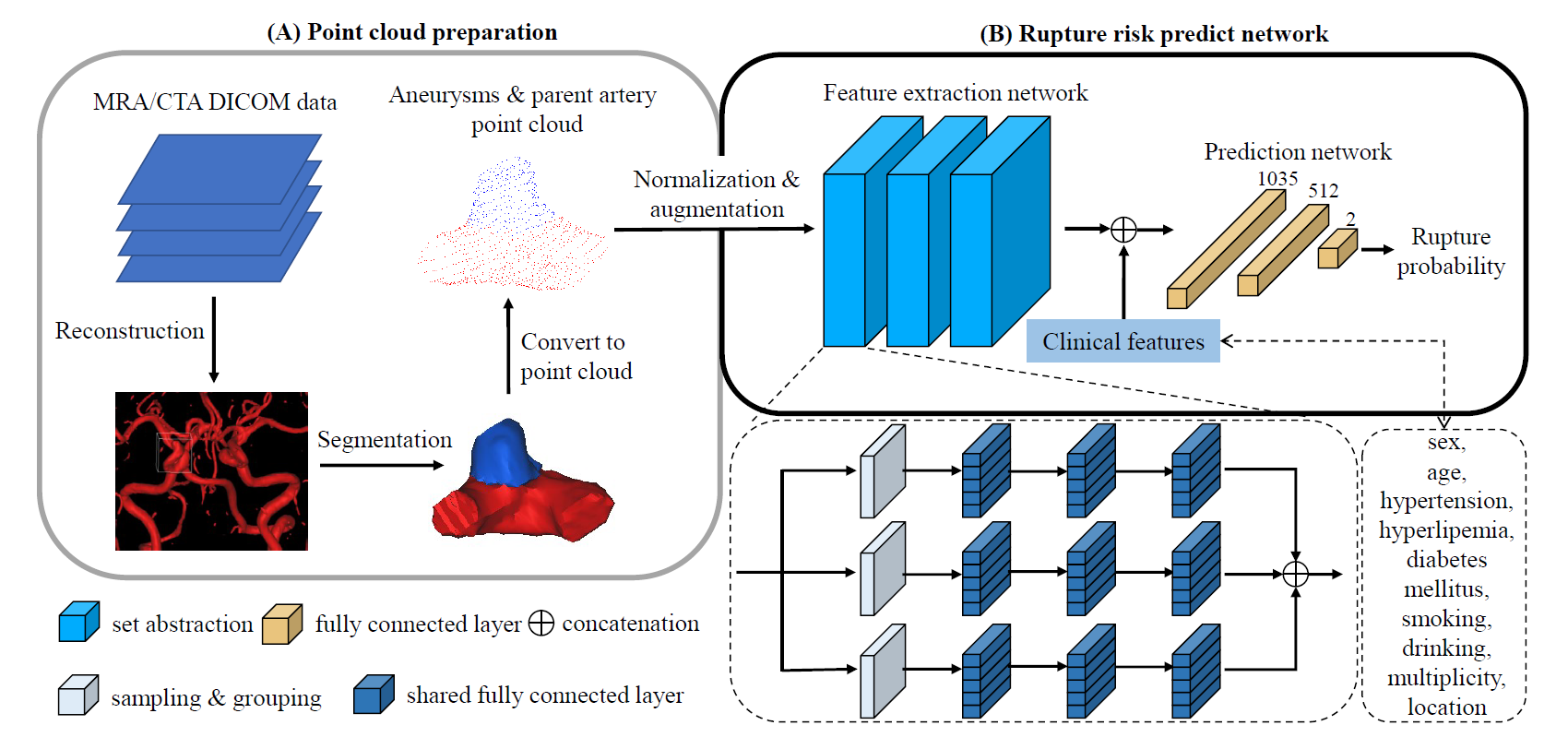
Objective: Accurate prediction of cerebral aneurysm (CA) rupture is of great significance. We intended to evaluate accuracy of the point cloud neural network (PC-NN) in predicting CA rupture using magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and computed tomography angiography (CTA) data.
Methods: 418 CAs in 411 consecutive patients confirmed by CTA (n=180) or MRA (n=238) in single hospital was retrospectively analyzed. A PC-NN aneurysm model with/without parent artery involvement was used for CA rupture prediction and compared with ridge regression, support vector machine (SVM) and neural network (NN) models based on radiomics features. Furthermore, the performance of the trained PC-NN and radiomics-based models was prospectively evaluated in 258 CAs of 254 patients from five external centers.
Results: In the internal test data, the area under the curve (AUC) of the PC-NN model trained with parent artery 0.913 was significantly higher than that of the PC-NN model trained without parent artery (AUC=0.851; P=0.041) and of the ridge regression (AUC=0.803; P=0.019), SVM (AUC=0.788; P=0.013) and NN (AUC=0.805; P=0.023) radiomics-based models. Additionally, the PC-NN model trained with MRA source data achieved a higher prediction accuracy (AUC=0.936) than that trained with CTA source data (AUC=0.824; P=0.043). In external data of prospective cohort patients, the AUC of PC-NN was 0.835, significantly higher than ridge regression (0.692; P<0.001), SVM (0.701; P<0.001) and NN (0.681; P<0.001) models.
Conclusion: PC-NNs can achieve more accurate CA rupture prediction than traditional radiomics-based models. Furthermore, the performance of the PC-NN model trained with MRA data was superior to that trained with CTA data.