Label correlation transformer for automated chest X-ray diagnosis with reliable interpretability
Zexuan Sun*, Linhao Qu*, Jiazheng Luo, Zhijian Song†, Manning Wang†
La radiologia medica (IF=6.313)
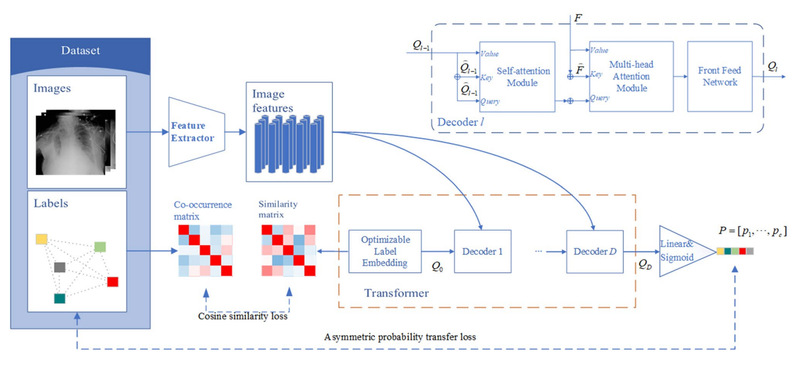
Computer-aided diagnosis of chest X-ray (CXR) images can help reduce the huge workload of radiologists and avoid the inter-observer variability in large-scale early disease screening. Recently, most state-of-the-art studies employ deep learning techniques to address this problem through multi-label classification. However, existing methods still suffer from low classification accuracy and poor interpretability for each diagnostic task. This study aims to propose a novel transformer-based deep learning model for automated CXR diagnosis with high performance and reliable interpretability. We introduce a novel transformer architecture into this problem and utilize the unique query structure of transformer to capture the global and local information of the images and the correlation between labels. In addition, we propose a new loss function to help the model find correlations between the labels in CXR images. To achieve accurate and reliable interpretability, we generate heatmaps using the proposed transformer model and compare with the true pathogenic regions labeled by the physicians. The proposed model achieves a mean AUC of 0.831 on chest X-ray 14 and 0.875 on PadChest dataset, which outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods. The attention heatmaps show that our model could focus on the exact corresponding areas of related truly labeled pathogenic regions. The proposed model effectively improves the performance of CXR multi-label classification and the interpretability of label correlations, thus providing new evidence and methods for automated clinical diagnosis.