Segmentation of Multi-Regional Skeletal Muscle in Abdominal CT Image for Cirrhotic Sarcopenia Diagnosis
Genshen Song, Ji Zhou, Kang Wang, Demin Yao, Shiyao Chen†, Yonghong Shi†
Frontiers in Neuroscience (IF=5.152)
Background Sarcopenia is generally diagnosed by the total area of skeletal muscle in the CT axial slice located in the third lumbar (L3) vertebra. However, patients with severe liver cirrhosis cannot accurately obtain the corresponding total skeletal muscle because their abdominal muscles are squeezed, which affects the diagnosis of sarcopenia.
Purpose This study proposes a novel lumbar skeletal muscle network to automatically segment multi-regional skeletal muscle from CT images, and explores the relationship between cirrhotic sarcopenia and each skeletal muscle region.
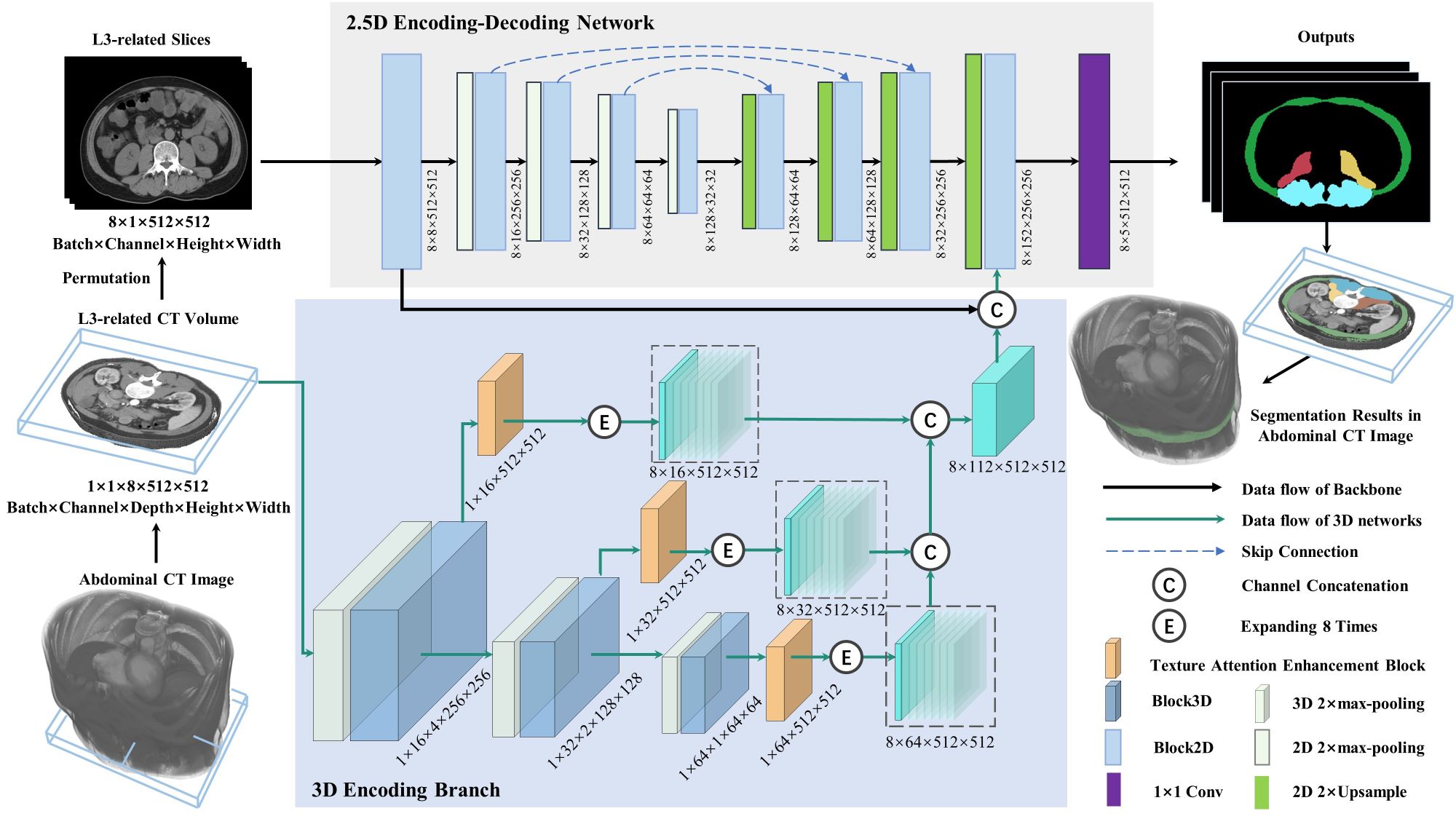
Methods This study utilizes the skeletal muscle characteristics of different spatial regions to improve the 2.5D U-Net enhanced by residual structure. Specifically, a 3D texture attention enhancement block is proposed to tackle the issue of blurred edges with similar intensities and poor segmentation between different skeletal muscle regions, which contains skeletal muscle shape and muscle fibre texture to spatially constrain the integrity of skeletal muscle region and alleviate the difficulty of identifying muscle boundaries in axial slices. Subsequentially, a 3D encoding branch is constructed in conjunction with a 2.5D U-Net, which segments the lumbar skeletal muscle in multiple L3-related axial CT slices into four regions. Furthermore, the diagnostic cut-off values of the L3 skeletal muscle index (L3SMI) are investigated for identifying cirrhotic sarcopenia in four muscle regions segmented from CT images of 98 patients with liver cirrhosis.
Results Our method is evaluated on 317 CT images using the five-fold cross-validation method. For the four skeletal muscle regions segmented in the images from the independent test set, the avg DSC is 0.937 and the avg surface distance is 0.558 mm. For sarcopenia diagnosis in 98 patients with liver cirrhosis, the cut-off values of Rectus Abdominis, Right Psoas, Left Psoas, and Paravertebral are 16.67, 4.14, 3.76, and 13.20 cm2/m2 in females, and 22.51, 5.84, 6.10, and 17.28 cm2/m2 in males, respectively.
Conclusions The proposed method can segment four skeletal muscle regions related to the L3 vertebra with high accuracy. Furthermore, the analysis shows that the Rectus Abdominis region can be used to assist in the diagnosis of sarcopenia when the total muscle is not available.