Deep-learning-based 3D multi-view multi-parametric MRI fusion model for preoperative T-staging of rectal cancer
Biomedical Signal Processing and Control (IF=4.9)
Abstract
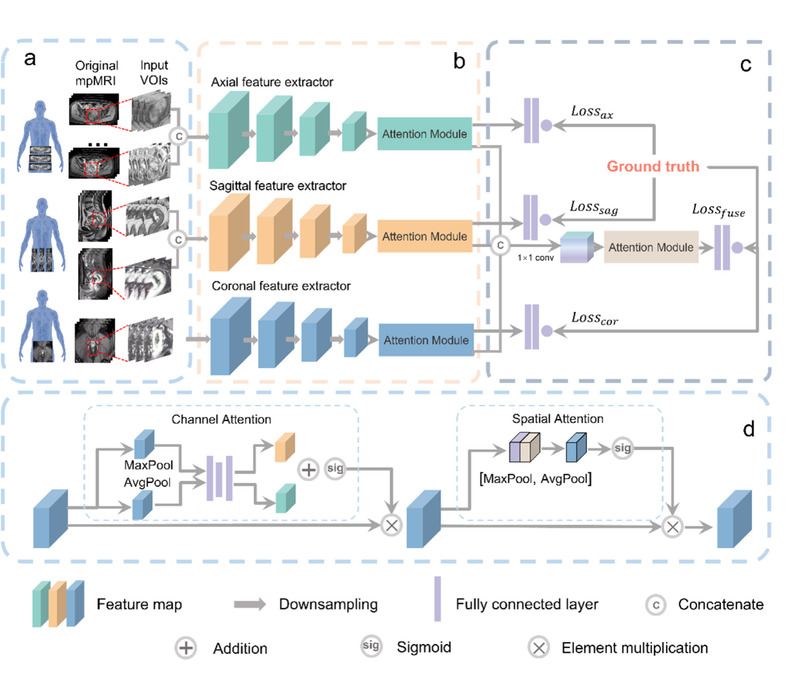
Deep learning (DL) approaches leveraging multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) hold significant promise for the preoperative assessment of rectal cancer T-stage. In this study, we investigate whether a mpMRI fusion-based DL model can effectively evaluate the T-stage of rectal cancer. To enable robust development and comprehensive evaluation of an automated T-staging system, we assembled the largest mpMRI cohort to date, comprising 756 patients from three institutions with nine distinct imaging sequences. We introduce a multi-view multi-parametric (MVMP) MRI fusion model for this purpose. The strategy for effective sequence fusion involves grouping different MRI sequences based on scanning directions and integrating features from each group using an attention module. During evaluations, the MVMP model achieves performance comparable to that of two radiologists in both the internal test cohort (AUC: 0.84 vs. 0.79 vs. 0.79) and the external test cohort (AUC: 0.83 vs. 0.81 vs. 0.75). Moreover, it outperforms other DL competitors in both the internal (AUC: 0.840 vs. 0.766 vs. 0.787) and external test cohorts (AUC: 0.826 vs. 0.792 vs. 0.821). The validity of our design is further substantiated through ablation studies on backbone networks, view-specific branches, and individual sequences. In summary, our DL model based on mpMRI and multi-view fusion accurately evaluates the preoperative T-stage of rectal cancer and shows great promise as a valuable tool for clinical assessment.