

An artificial intelligence-driven image quality assessment system for whole-body [18F]FDG PET/CT
Chi Qi*, Shuo Wang*, Haojun Yu, Yiqiu Zhang, Pengcheng Hu, Hui Tan, Yonghong Shi†, Hongcheng Shi†
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (IF=10.057)
Purpose. Image quality control is a prerequisite for applying PET/CT. This study aimed to develop an artificial intelligence-driven real-time and accurate whole-body [18F]FDG PET/CT image quality assessment system.
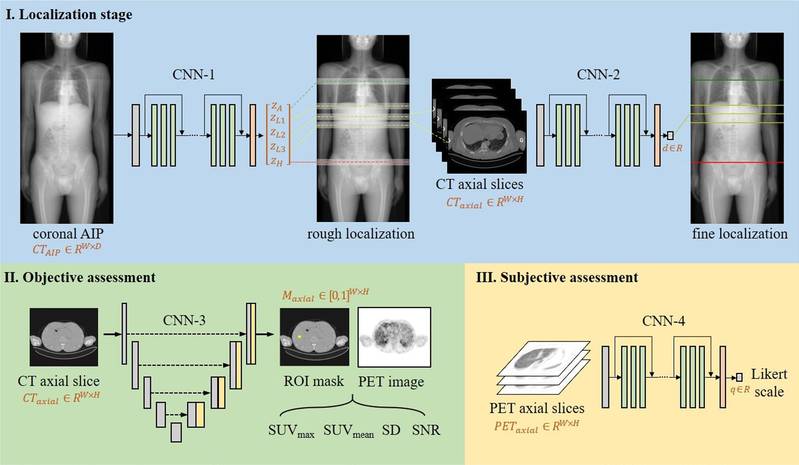
Methods. This study included 173 patients (age, 59 ± 12 years; 66.3% males) with whole-body [18F]FDG PET/CT imaging. Images of ten patients were used as an educational set. Images of the rest 163 patients were reconstructed to 952 images by simulating several scanning times and randomly split into training (60%, 98 patients, 578 images), validation (20%, 33 patients, 192 images), and test (20%, 32 patients,182 images) sets. Two experienced physicians (R1 and R2) independently assessed the image quality of thorax, abdomen, and pelvis region twice (R1a and b; R2a and b), 1 month apart, using a 5-point Likert scale. Objective image quality metrics were extracted from the mediastinal blood pool, three liver levels, and the bilateral gluteus maximus. The developed convolutional neural networks for image quality assessment (IQA-CNNs) generated the subjective quality scores and objective image metrics. The IQA-CNNs and physicians’ performances were compared for localization accuracy, score agreement, and process time.
Results. The physicians demonstrated good inter- and intra-rater subjective assessment agreement, with kappa coefficients (R1a vs. R2a, R1a vs. R1b, R2a vs. R2b, and R1a vs. R2b) of 0.78, 0.77, 0.76, and 0.80. The IQA-CNNs and R1 or R2 agreed in the subjective assessments, with kappa coefficients of 0.79 and 0.78. IQA-CNNs and R1 or R2 also agreed in their objective image quality assessment (ICC > 0.60). The IQA-CNNs evaluation speed was 200 times faster than the manual assessment.
Conclusion. An automated system for rapid assessment of [18F]FDG PET/CT image quality was developed, showing comparable performance to senior physicians. The system generates a comprehensive and detailed image quality assessment report, including subjective visual scores and objective image metrics for various anatomical regions.
本文共同第一作者为复旦大学附属中山医院核医学科漆赤医师和实验室王烁青年研究员,共同通讯作者为实验室史永红副教授和复旦大学附属中山医院核医学科石洪成教授。